Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to the set of business practices that meet or exceed the economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic expectations of society. It includes the overall relationships of the organization with all its stakeholders. For that reason, public authorities, organizations, and consumers increasingly demand that companies contribute greater benefits to society and measure their positive and negative impacts within it. CSR is intrinsically linked to the concept of sustainable development and the management of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of the operations of organizations.
Quality management practices facilitate the development of environmental management, require ethical behavior, stakeholder focus, and may facilitate the development of activities that are socially responsible. And all the above must be achieved within the terms of competitiveness. This has brought about certain pressure to integrate the principles of CSR into quality management systems. Excellence Models are used to implement the principles and practices of quality management. The established Excellence Models, such as the European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) Excellence Model, and others, all incorporate a social responsibility element, and advocate management practices compatible with the ideals of CSR.
Can a company simultaneously align its Quality Management and CSR objectives and practices?
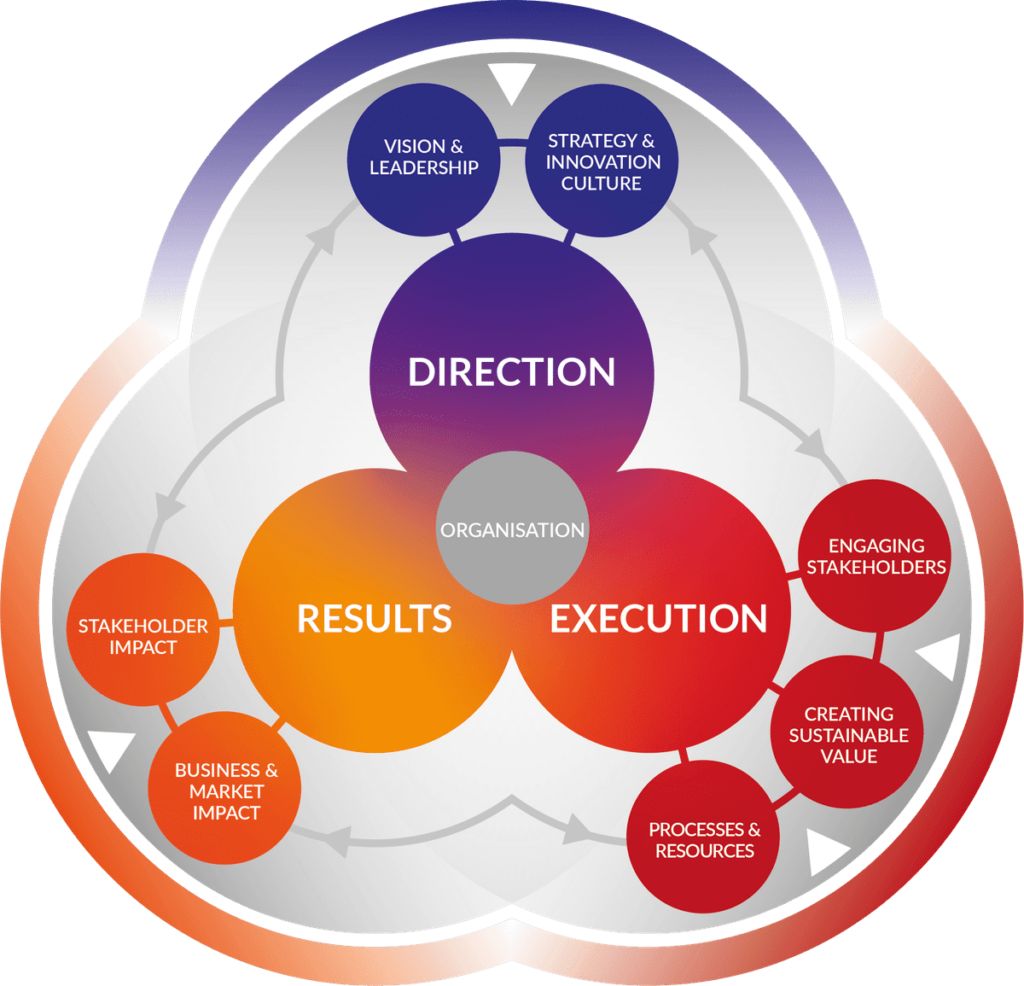
EFQM is a comprehensive organizational management approach. This approach is based on the correct integration of certain cultural values and principles (continuous improvement, innovation, and dynamism) into the strategy, structure, and processes of the organization. To put these values and principles into practice, organizations use a series of techniques, models, and systems oriented towards stakeholder satisfaction and strengthening the competitiveness of the organization. Among the critical factors of EFQM are an organizational culture oriented to continuous improvement; a determined commitment and leadership by the management; strategic planning; continuous improvement; a customer- and other stakeholder-focused approach; management based on data and information analysis; and the management of personnel, processes and suppliers or other partners.
On the other hand, CSR is defined as the commitment of an organization to assess and to take responsibility for the impacts that its decisions and activities have on society and the environment, by means of an ethical and transparent behavior that takes into consideration the interests of all parties, fulfils the applicable legislation and is consistent with international standards of behavior, and is integrated into the whole organization and put into practice in its relationships.
Continuous improvement of quality requires a commitment to exceed the expectations of the customers and other stakeholders. CSR has a positive impact on the progress of businesses, as it reduces litigations, protects the brand image, improves customer satisfaction, and reduces absenteeism and employee turnover, whilst retaining the personnel with the most talent. CSR approaches aspects such as employee satisfaction, protection of the environment, and sustainability so that it can be defined in terms of acceptable ethical behavior and, second, can be seen from an instrumental perspective in which the image and the goals of the organization are a primary concern. In short, EFQM is consistent with the ethical aspect and vision of CSR. This suggests that CSR can be incorporated into organizations more effectively, and in less time, by using the existing values, principles, and practices of EFQM.
The EFQM Excellence Model has a flexible nature and can be applied to large and small organizations, in the public and private sectors, as well as to industrial and service companies. In addition, it is a dynamic model that has evolved and adapted to social changes.
The base for the application of the model and the improvement of the management is self-assessment. Self-assessment measures the level of quality reached in an organization through a series of criteria and management and performance indicators. Once the self-assessment has been made, the organization can opt for certain stamps of recognition or may even choose to present a candidacy for different quality awards. For this, it will have to be subjected to a process of external assessment by independent experts who will make a detailed analysis before they verify the self-assessment report presented by the organization.
The EFQM model incorporates the growing importance of the CSR and sustainability for the management excellence in the organizations. It includes topics such as positive impact in the organization, and accountability.

Social impact and fundamental concepts of excellence
Excellent organizations adopt a strict ethical approach, are transparent, and are accountable to their stakeholders for their performance as responsible organizations. They consider and promote social responsibility and environmental protection.
The social responsibility of organizations is defined in their values and integrated into their strategies by means of public and transparent commitments, which includes all stakeholders. In addition, they satisfy and exceed the expectations, standards, and laws that are applicable to them. Also, they manage risks, and they seek and promote opportunities to collaborate with society in mutually beneficial projects, promoting and maintaining a high level of confidence among their stakeholders. They are aware of their impact on the present and future community and they are concerned about reducing any adverse impact to the minimum.
Social impact and the EFQM Excellence Model
The EFQM model entails that excellent organizations take extensive measures and reach excellent results with respect to society, including the collaboration of the organization with philanthropic activities, relationships with authorities, ethics, social responsibility, environment protection, etc.
CSR and sustainability have a strong presence in EFQM. The EFQM Excellence Model includes the most significant aspects of CSR, such as: community relations, social responsibility and new opportunities, minorities/diversity and working conditions, ethics awareness, education and training, consumer relations, natural environment, supplier relations, and the physical environment.
The leadership and the human resources are considered determining factors for the success of the quality management and CSR initiatives. Thus, the management must act as a guide and driver in the process of implementation of the EFQM Excellence Model, and must create and spread the values of excellence in management, as well as establishing goals and objectives that are consistent with these values.
From the CSR perspective, leaders must consider the needs of all stakeholders, creating models of ethical and socially responsible behavior at all levels of the organization. However, to achieve success, management commitment alone is not sufficient, but its involvement must also be demonstrated through investment in different resources (material, financial, knowledge, and technological) which support the attainment of the objectives and the improvement of all the processes.
In addition, the organization, through the management and its leaders, must try to obtain the commitment and involvement of all the personnel and, in return, to empower their participation in the decision-making and improvement activities.
To achieve this, the leaders must influence their employees, not only through the more technical aspects of the work, but also through the psycho-emotional and ethical dimensions of the work. These actions will lead to the correct execution and improvement of the processes of the organization, which will lead to improved results.
Finally, the crucial role played by the management and human resources in the formulation, deployment, implementation, and control of the policies and strategies of the organization must not be forgotten.
Companies which wish to improve their results and their social impact must take into account that social factors in quality management are the most important.
If an organization is interested to satisfy the expectations of the relevant people and institutions, it must build into its strategy both social responsibility and ways to measure its impact on the society where it operates.
Although organizational ethics is a subjective matter, quality management includes recognition of certain social standards and includes them in its strategy.
This may lead to sacrifice of short-term profits in the interest of the opportunity to show attitudes which contribute to a positive social image of the organization. In a broader sense, the management and continuous improvement of quality involve considering the social customer as consisting of the different segments that constitute the organizational macro-environment (political-legal, economic, environmental, and sociocultural).
In addition, the organization must not forget that the relationships with its stakeholders are based on a balance between the rights and obligations; that is, they must not only receive, but also give. The balance between the interests of the society and the company will ultimately lay the foundations of a socially responsible behavior and quality management.